OMIGOD- Critical Vulnerabilities in OMI Affecting Countless Azure Customers
Introduction Among Google cloud, IBM, and AWS, Microsoft Azure was cited as the most trusted public cloud. The Covid-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of cloud computing with multiple companies migrating to the cloud providers, especially Microsoft’s Azure, cites this new research. OMI doesn’t come with VMs, but we are installing them on top of the […]
Reading Time: 3 minutes
Table of Contents
Introduction
Among Google cloud, IBM, and AWS, Microsoft Azure was cited as the most trusted public cloud. The Covid-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of cloud computing with multiple companies migrating to the cloud providers, especially Microsoft’s Azure, cites this new research.
OMI doesn’t come with VMs, but we are installing them on top of the virtual machine. Most of the users use these convenient purposes. Recently, azure has been affected by four critical vulnerabilities in OMI. Which is one of Azure’s almost every yet least known software agent and is deployed on a vast portion of Linux VMs in Azure.
- CVE-2021-38647 — Unauthenticated RCE as root
- CVE-2021-38648 — Privilege Escalation Vulnerability
- CVE-2021-38645 — Privilege Escalation Vulnerability
- CVE-2021-38649 — Privilege Escalation Vulnerability
These are the CVE details for OMI critical vulnerabilities, which are very easy to exploit, and the attacker will launch an attack within the network by remotely executing an arbitrary code with a single request, and he will gain the root privileges.
What is OMI?
Open Management Infrastructure (OMI) is an open-source Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) implementation for managing Linux and UNIX systems. Several Azure Virtual Machine (VM) management extensions use this framework to orchestrate configuration management and log collection on Linux VMs.
The remote code execution vulnerability only impacts customers using a Linux management solution (on-premises System Center Operations Manager (SCOM or Azure Automation State Configuration or Azure Desired State Configuration extension) that enables remote OMI management.
OMI is an agent which is automatically deployed on azure VMs as a segment in the onboarding process, which allows the users to handle the configurations across remote and local environments and collect statistics.
OMI is UNIX/Linux, similar to Windows WMI. OMI agents are normally used on-premises for the management of Linux machines. OMI is set up into Microsoft System Center for Linux, Microsoft’s server management solution.
Who is Vulnerable
Most massive organizations using Azure are affected. First and foremost, any customer using one or more of the following services:
- Azure Automation
- Azure Automatic Update
- Azure Operation Management Suite
- Azure Log Analytics
- Azure Configuration Management
- Azure Diagnostics
Note: these are some partial lists.
What versions of OMI are vulnerable?
All OMI versions below v1.6.8-1 are vulnerable.
How to identify your virtual machine with open management infrastructure (OMI)
Identify your VMs with OMI agents
The first step is to gather a list of all of your Azure VMs that have the OMI agent installed on them.
1. Connect to your Azure VMs and run in the terminal:
a. For Debian systems (e.g., Ubuntu): dpkg-I omi
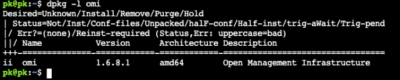
b. For Redhat-based systems (e.g., Fedora, CentOS, RHEL): rpm-qa omi
![]()
If OMI isn’t installed, no results will return, and your machine isn’t vulnerable to OMIGOD.
2. If results return, you’ll be able to see what the installed OMI version on your machines is. Version 1.6.8.1 is the patched version.
How can we mitigate an OMI attack?
To mitigate this vulnerability Microsoft is providing the tool to check whether your VMs are vulnerable or not to this attack. To perform this download the following GitHub URL https://github.com/microsoft/OMS-Agent-for-Linux in cloud shell. (This tool detects vulnerable OMI installations (< 1.6.8.1) in your subscriptions). SSH into VMs in the cloud shell.
Solutions for Cloud
Automatic: On September 17, 2021, Microsoft announced an auto-update feature for OMI agents installed as part of Azure cloud services. According to the announcement, the auto-update process should be completed by September 22, 2021.
Manual Update
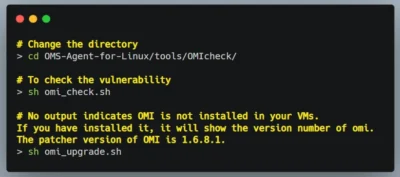
Change the directory
cd OMS-Agent-for-Linux/tools/OMIcheck/
To check for Vulnerability
sh omi_check.sh
iff you don’t get any output, it means you don’t have omi installed in your VMs. If you have installed it, it will show the version number of omi. The patched version of OMI is 1.6.8.1.sh omi_upgrade.sh
If OMI is not installed in your VM, it will install automatically but if you have a running vulnerable version, it will automatically upgrade to the latest stable version.
On-premise Solutions:
Microsoft provides on-premises installations, along with specific additional products, that still require manual updating of the OMI package.
For more information on how to protect against OMIGOD vulnerability, do refer to this blog:
Thank You!
Conclusion
Now you can protect your workloads in minutes using AccuKnox, it is available to protect your Kubernetes and other cloud workloads using Kernel Native Primitives such as AppArmor, SELinux, and eBPF.
Let us know if you are seeking additional guidance in planning your cloud security program.
Get The Best Developer and Security ROI
Zero Trust Security
Code to Cloud
AppSec + CloudSec

Prevent attacks before they happen
Schedule 1:1 Demo